Oftentimes, the latest fashion trends heavily influence people’s wardrobe choices. However, some fashionistas prefer sustainable clothing for durability over style. This is where the slow fashion vs. fast fashion debate comes into play.
In this article, we’ll discuss all of the key differences between slow fashion vs fast fashion, including their pros and cons, so stick around!
Key Differences Between Slow Fashion and Slow Fashion

Fast fashion focuses on the number of products that make it to the market in a short period of time. Some brands that adopt this approach include Zara, SHEIN, and H&M.
In contrast, slow fashion is a countermovement of fast fashion. It’s a business model in the fashion industry where they have a cautious and sustainable approach to fashion. Sustainable fashion cares about quality over quantity. Slow fashion brands include Quince, Reformation, and Eileen Fisher.
Aside from that, here are the major aspects that differentiate slow and fast fashion:
1. Goal
The main goal of fast fashion is to produce and sell a huge number of items in a short period of time. Fast fashion brands want to make as much profit as they can, regardless of the number of hours and amount of labor they have to put into the production.
Slow fashion companies do the opposite. Slow fashion garments are produced more ethically and sustainably. The production of the slow fashion industry takes longer because there is clothing made by hand or locally produced.
2. Materials

Typically, fast fashion companies use synthetic materials, like petroleum-based fibers. Some examples are polyester, nylon, and acrylic. These are cheap materials and they’re also made from nonrenewable fossil fuels.
In comparison, slow fashion aims for high-quality materials for production. Most brands use natural fibers like cotton, sheep’s wool, silk, and cashmere.
Related Content: Top 6 Sustainable Clothing Materials To Look Out For
3. Production
When it comes to production, fast fashion companies produce more items compared to their slow fashion counterparts. They often have an extensive target market and an overabundance of inventory.
In the present day, fast fashion firms produce approximately 52 micro-seasons yearly, which is equivalent to one new collection every week.
On the other hand, slow fashion has slower production. In fact, most brands produce at least one capsule collection per year because they embrace designing seasonless fashion. For instance, Ouisa annually releases two six-piece capsule collections.
Related Content: 4 Tips For Building A School Capsule Wardrobe That’s Cute And Comfy
4. Effects on the Environment and Consumers

Since the fast fashion industry uses fibers made from crude oil, it poses a negative impact on the environment. Petroleum-based fibers can emit significant amounts of carbon dioxide during production. Consequently, it increases greenhouse gas emissions.
Fast fashion firms are also responsible for water pollution because the fibers are released into the ocean as microplastics.
Aside from that, they also use hazardous chemicals such as PFAS, Azo dyes, and phthalates. Some of them have milder effects like eye and skin irritation. Unfortunately, chemicals like PFAS have carcinogenic effects.
In contrast, slow fashion is considered environmentally friendly because they opt out of synthetic materials. For instance, cork fabric has become a popular material for vegan shoes and bags.
The cork plantation is considered a carbon sink because the fabric is harvested from cork oaks by shaving away their bark. Then, while the trees are regrowing their barks, they absorb more carbon dioxide, which can help reduce climate change.
Moreover, other natural materials like organic hemp and peñatix also consume carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. That’s why they’re one of the most eco-friendly fibers in the industry.
5. Impact on Human Labor
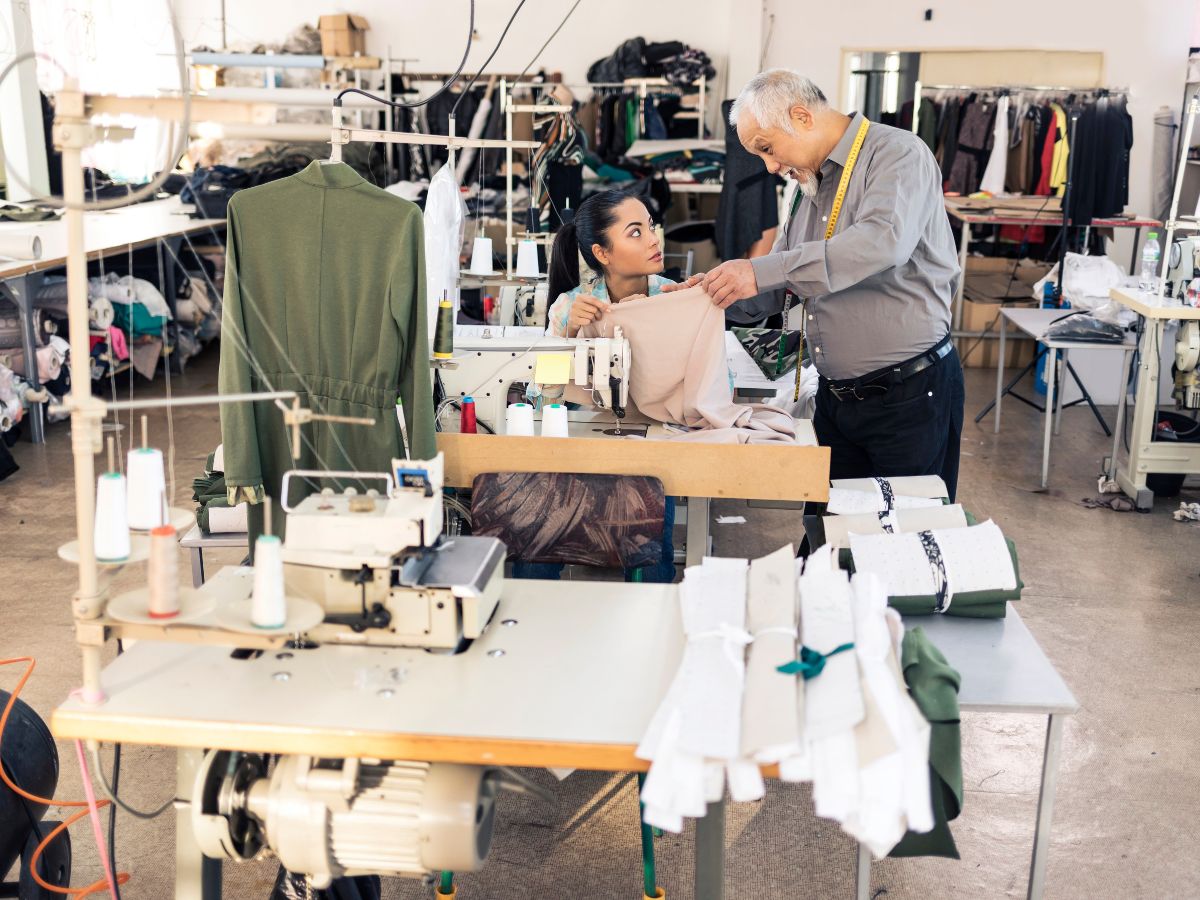

The fast fashion industry has an increasing demand for delivery dates and short production cycles. This mostly puts pressure on its workers.
For instance, due to the competition in the market, garment factories need to keep up with the high demand at the expense of their workers. Some examples of its negative effects are low income and poor working conditions. In fact, some lead to tragic fires and accidents.
In comparison, slow fashion firms produce fashion often with regard to its effect on their workers and human rights. They counteract the methods of their fast fashion counterparts by treating their workers fairly.
6. Style and Quality
Usually, fast fashion products are trendy and stylish. Unfortunately, the pieces aren’t designed to last more than one to two washes. Some consumers even throw them away after a couple of wears. Fast fashion looks quickly go out of style because of the rapid trend cycles.
Slow fashion, on the other hand, releases garments that you can wear far longer because of their good quality materials. However, companies keep their designs simple. Although some fashionistas might find them dull, they’re more durable and better in quality. This helps you not have to buy new clothes as often since their life cycle is much longer.
7. Affordability

Due to the more affordable materials of fast fashion products, they usually come at extremely low prices. However, even if items are cheap, consumers’ excessive shopping tends to add up to a significant cost.
Plus, people try to keep up with the constant changes in fashion trends. As a result, they spend more on clothes. However, these garments only end up in landfills after a few wears.
Studies show that 85% of fast fashion clothes end up as solid waste sent to landfills per year, amounting to nearly 80 pounds of garments per American.
In contrast, slow-fashion clothing costs more than fast-fashion items. However, they’re not necessarily expensive in the long run. You can save more because you won’t have to replace them constantly.
This is one of the most obvious differences in slow fashion vs fast fashion that people notice.
8. Consumption
Fast fashion offers several collections that eventually go out of style. While affordability allows more access for those fashionistas with lower incomes, it often leads to over-consumption or excessive shopping.
In comparison, consumers who purchase from slow fashion, get more sustainable items. Companies release clothing with less trendy designs and high-quality materials. As a result, they last for a long time. This way, consumers buy less and decrease consumption.
What’s more, the slow fashion movement also advocates clothes manufactured with respect to the environment, animals, and workers.
9. Availability
The fast fashion industry is known for its mass production. In just a few months, they release seasonal collections that are available in just weeks.
The large quantities make the items more accessible even to young consumers because they offer more sizes, colors, prices, and styles. Although the pieces are the current trend in the fashion world, they typically become disposable once the trend dies out.
In comparison, slow fashion has timeless designs, so consumers can purchase them regardless of the latest trend. Unlike fast fashion though, they’re available in smaller local stores rather than in large chain enterprises.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Fast Fashion?
According to the Fast Fashion Global Market Report in 2021, the size of the fast fashion market is expected to increase from $30.58 billion to $39.84 billion in 2025.
So, before you head to the biggest fashion retailers, it’s important that you know these pros and cons of fast fashion:
Pros
- More affordable
- Trendy/Stylish
- Accessible
- Quick production
Cons
- Negative impact on human labor
- Contributes to climate change
- Low quality
What Are the Pros and Cons of Slow Fashion?
Kate Fletcher, a design activist and journalist, coined the term ‘slow fashion’ as an antithesis of fast fashion. She also outlined the need to reevaluate the way consumers and manufacturers look at the fashion industry. Since then, the slow fashion movement has earned its popularity.
Here are the pros and cons of slow fashion:
Pros
- Environmentally friendly supply chain
- Durable
- Cost-efficient
- High quality
- Fair treatment of workers
- Fair wages
Cons
- Simple Designs
- More Expensive
Wrapping Up
The major differences between fast fashion vs. slow fashion are its goal, materials used in production, effects on the environment and its consumers, impact on human labor, Style, and quality.
It’s also worth noting that they’re also different when it comes to availability, consumption, and affordability. Therefore, it’s important that you inspect their pros and cons before you decide on your fashion choices.
Pin this image so you can find this post about slow fashion vs fast fashion for later!